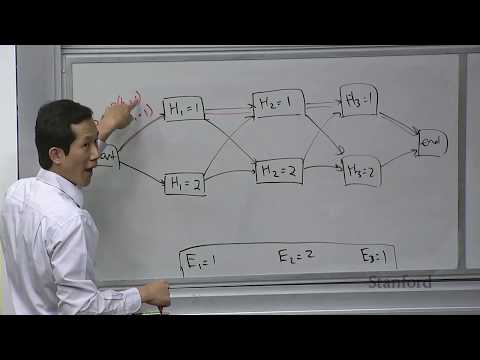
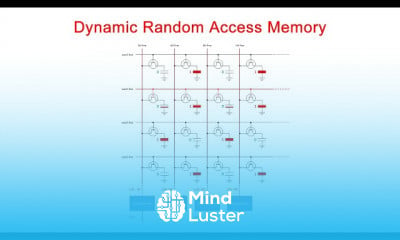
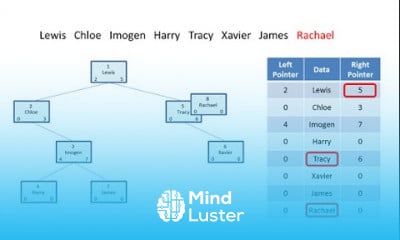
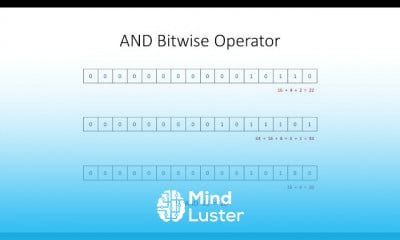
Lecture 14 Bayesian Networks 2 Forward Backward | Stanford CS221 AI Autumn 2019
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 19
Lesson
Comments
Related Courses in Computer Science
Course Description
What are the four key principles of responsible AI?
Answer: Their principles underscore fairness, transparency and explainability, human-centeredness, and privacy and security.Artificial intelligence is intelligence demonstrated by machines, unlike the natural intelligence displayed by humans and animals, which involves consciousness and emotionality. The distinction between the former and the latter categories is often revealed by the acronym chosen. Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. The term may also be applied to any machine that exhibits traits associated with a human mind such as learning and problem-solving.What is artificial intelligence with examples?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer sciences that emphasizes the development of intelligence machines, thinking and working like humans. For example, speech recognition, problem-solving, learning and planning.What are the 4 types of AI?
An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: The Four Types of AI
Reactive Machines. Reactive machines are the simplest level of robot. ...
Limited Memory. A limited memory machine, as the name might suggest, is able to retain some information learned from observing previous events or data. ...
Theory of Mind. ...
Self-awareness.
Trends
Graphic design tools for beginners
Web design basics
Figma for UX UI design
Make money as a freelance designer
Logo design with circles in Illustrator
Best zoology books
UX UI design career
Freelance graphic design business
Illustrator poster design for beginners
Master graphic design techniques
Design Pie charts in figma
Figma heart icon design
Mastering logo design in illustrator
Figma design basics for beginners
Illustrator for logo design beginners
Setting Up illustrator for logo design
Figma mobile UI design essentials
Financial Accounting basics
Figma glassmorphism sidebar design
Source documents in accounting beginners
Recent
Bioinformatics basics
Bioinformatics databases
Vitamin A to Z tablets
Best zoology books
Best cream for piles pain
Laser surgery for piles
Best cream for piles
Anal fissure treatment
Best antibiotics for diseases
Antibodies structure
Macrophage structure
Drosophila genetics
Diagnostic tests
Bioinformatics
Genetics
Gene therapy
Kidney structure
DNA replication and types
Bacterial cell structure
Parasite structure