Introduction to Data Base Management Systems DBMS Advantages Purposes Data Informati
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lesson extensions
Lessons List | 39
Lesson
Comments
Related Courses in Computer Science
Course Description
Data Models in DBMS in hindi course,
in this course we will learn about the data models in Database Management Systems (DBMS), which are fundamental for organizing, storing, and managing data efficiently. Data models define the logical structure of a database and establish the relationships among data elements. We will explore various types of data models, each suited for different types of applications and requirements.
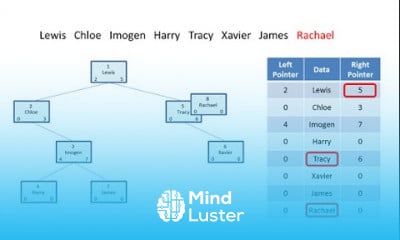
We will begin with the Hierarchical Data Model, which organizes data in a tree-like structure, where each child node has a single parent node, suitable for applications requiring a clear, parent-child relationship. Next, we will delve into the Network Data Model, which allows more complex many-to-many relationships through a graph structure.
The Relational Data Model is a cornerstone of modern databases, organizing data into tables (relations) with rows and columns, and using primary and foreign keys to establish relationships. The Entity-Relationship (ER) Model will be covered to help in designing relational databases by visually mapping out entities and their relationships.
We will also examine the Object-Oriented Data Model, which integrates object-oriented programming principles to handle complex data and relationships more naturally. The Object-Relational Data Model combines the relational model with object-oriented features to offer greater flexibility.
Trends
Management from A to Z
Learning English Speaking
MS Excel
Python programming language
Digital Marketing From Scratch
Adobe illustrator tools for designers
a Road Using Civil 3D
Ethical Hacking
Digital Marketing
Complete WIFI Hacking Course Beginner to Advanced
Graphic design rules for beginners
Mobile Apps from Scratch
Organization of Microcontroller
Photo Editing
C Programming Language
Human Resource Management
Advanced Soil Mechanics course
Human Resource Management in Public Service for mangers
Website security basics
SEO for business growth for beginners
Recent
Python mySQL database connection
Model deployment on unix for beginners
Data Science knowledge test
Data science mock interview basics
Deep Learning interview questions
VIF application in python for beginners
Data science basics quiz
NLP and generative AI for beginners
Linux command essentials from scratch
Aws for data science basics
Website security basics
SEO for business growth for beginners
WordPress migration on bluehost for beginner
Influencer marketing essentials
Increase eCommerce sales ways
Content marketing works in 2024
Local SEO for multi location businesses
Ranking with google AI tools
SearchGPT for SEO and content writing
AI marketing fundamentals