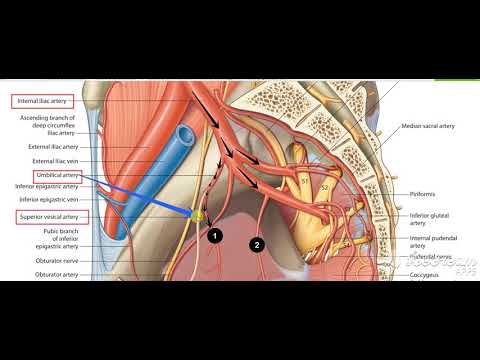
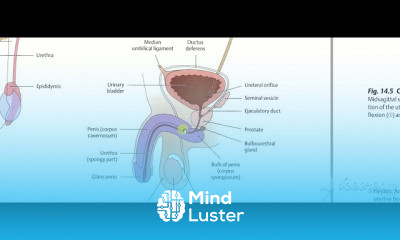
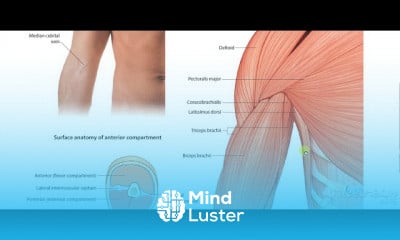
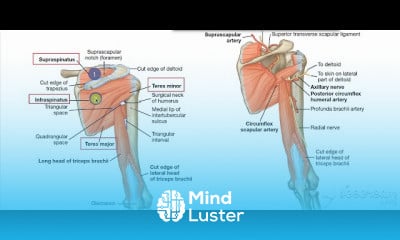
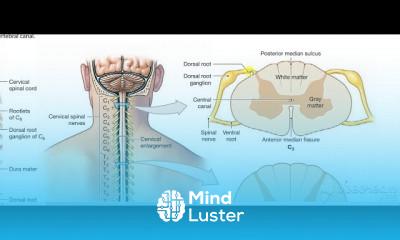
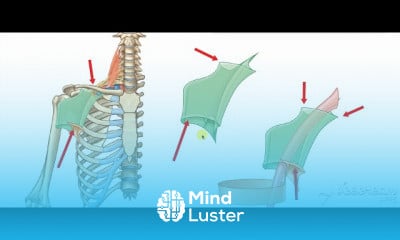
Urinary bladder arterial supply 2
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 54
Lesson
Show More
Lessons
Comments
Related Courses in Medical
Course Description
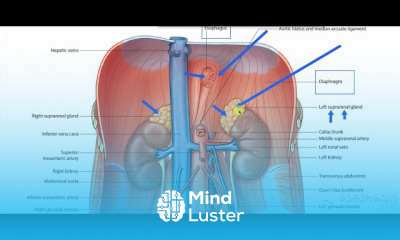
The urinary system, also known as the renal system or urinary tract, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes (in the form of urine) exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination (voiding). The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
Urine is formed in the kidneys through a filtration of blood. The urine is then passed through the ureters to the bladder, where it is stored. During urination, the urine is passed from the bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body.
800–2,000 milliliters (mL) of urine are normally produced every day in a healthy human. This amount varies according to fluid intake and kidney function.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system — your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men. Infection limited to your bladder can be painful and annoying. However, serious consequences can occur if a UTI spreads to your kidneys.
Doctors typically treat urinary tract infections with antibiotics. But you can take steps to reduce your chances of getting a UTI in the first place.
Trends
Graphic design tools for beginners
Human Resources Management
French
Artificial intelligence essentials
Electrical engineering for engineer
Java Basic Programming Hindi
Essential english phrasal verbs
CMOS Logic Circuit Basics
Bioinformatics basics
Build a profitable trading
MS Excel
Build a tic tac Toe app in Xcode
Computer science careers
Excel skills for math and science
Python programming language
American english speaking practice
Formation efficace à l écoute de l
Marketing basics for beginners
Content marketing for beginners
Figma for UX UI design
Recent
Bioinformatics basics
Bioinformatics databases
Vitamin A to Z tablets
Best zoology books
Best cream for piles pain
Laser surgery for piles
Best cream for piles
Anal fissure treatment
Best antibiotics for diseases
Antibodies structure
Macrophage structure
Drosophila genetics
Diagnostic tests
Bioinformatics
Genetics
Gene therapy
Kidney structure
DNA replication and types
Bacterial cell structure
Parasite structure