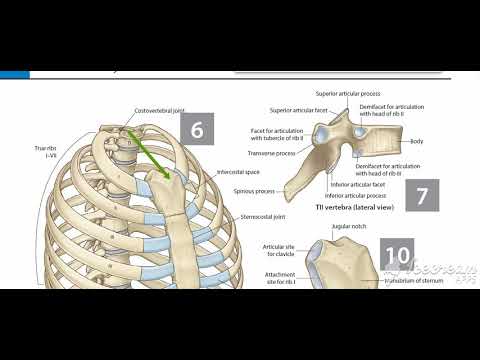
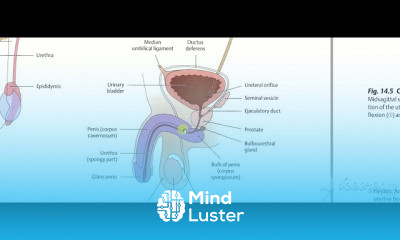
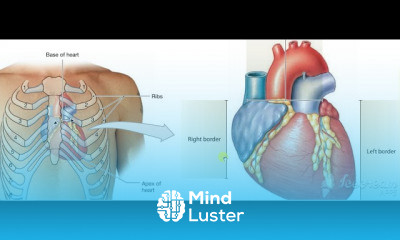
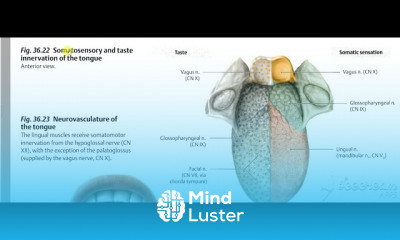
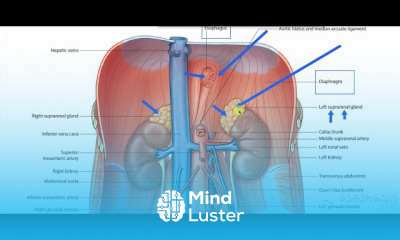
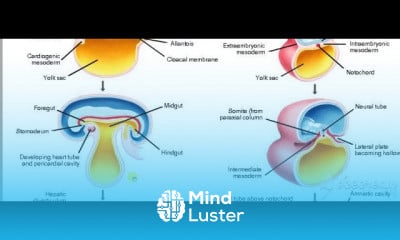
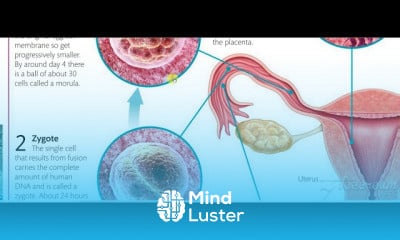
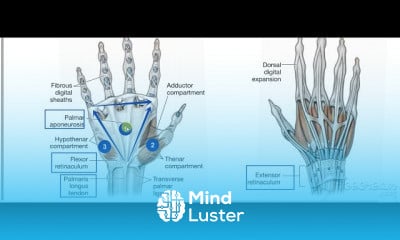
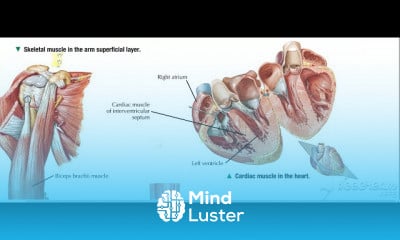
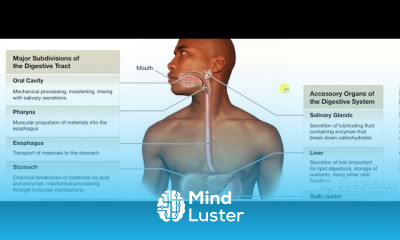
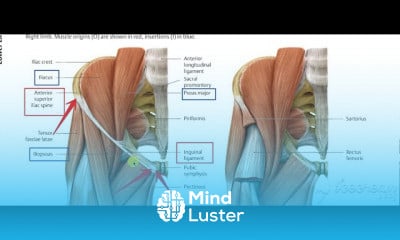
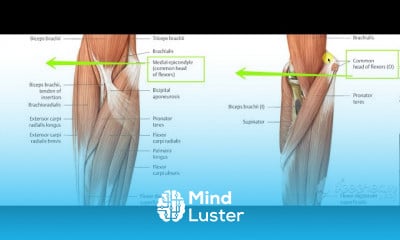
Thoracic cage 3
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 100
Lesson
Show More
Lessons
Comments
Related Courses in Medical
Course Description
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.
In most fish, and a number of other aquatic animals (both vertebrates and invertebrates) the respiratory system consists of gills, which are either partially or completely external organs, bathed in the watery environment. This water flows over the gills by a variety of active or passive means. Gas exchange takes place in the gills which consist of thin or very flat filaments and lammelae which expose a very large surface area of highly vascularized tissue to the water.
Other animals, such as insects, have respiratory systems with very simple anatomical features, and in amphibians even the skin plays a vital role in gas exchange. Plants also have respiratory systems but the directionality of gas exchange can be opposite to that in animals. The respiratory system in plants includes anatomical features such as stomata, that are found in various parts of the plant.
Trends
Graphic design tools for beginners
Financial Accounting
Web design basics
Advanced Logo design methods
Logo Design
Accounting Finance course
Figma for UX UI design
Customizing type for logos
Freelance graphic design business
Accounting
Graphic Design | Photoshop
UX design career in 2025
Best zoology books
Graphic Design Basics
Web Design 101 Free Full Course
Essential skills for web designers
SQL for accountants and finance managers
Mastering logo design in illustrator
Figma Signing Up and Signing In
Web Design Using HTML CSS
Recent
Bioinformatics basics
Bioinformatics databases
Vitamin A to Z tablets
Best zoology books
Best cream for piles pain
Laser surgery for piles
Best cream for piles
Anal fissure treatment
Best antibiotics for diseases
Antibodies structure
Macrophage structure
Drosophila genetics
Diagnostic tests
Bioinformatics
Genetics
Gene therapy
Kidney structure
DNA replication and types
Bacterial cell structure
Parasite structure